In the era of technological advancements, drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have emerged as a game-changer in agriculture.
This article explores how drones are transforming agriculture, their applications, benefits, challenges, and their potential to redefine rural farming practices.
1. The Need for Innovation in Agriculture
1.1. Challenges in Traditional Farming
Climate Change: Erratic weather patterns affect crop yields.
Labor Shortages: Migration and urbanization have led to a decline in available farm labor.
Resource Management: Inefficient use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides impacts both productivity and the environment.
1.2. Role of Technology in Addressing Challenges
Innovations like drones help bridge the gap by offering precision agriculture solutions, reducing resource wastage, and enabling better decision-making.
2. Applications of Drones in Agriculture
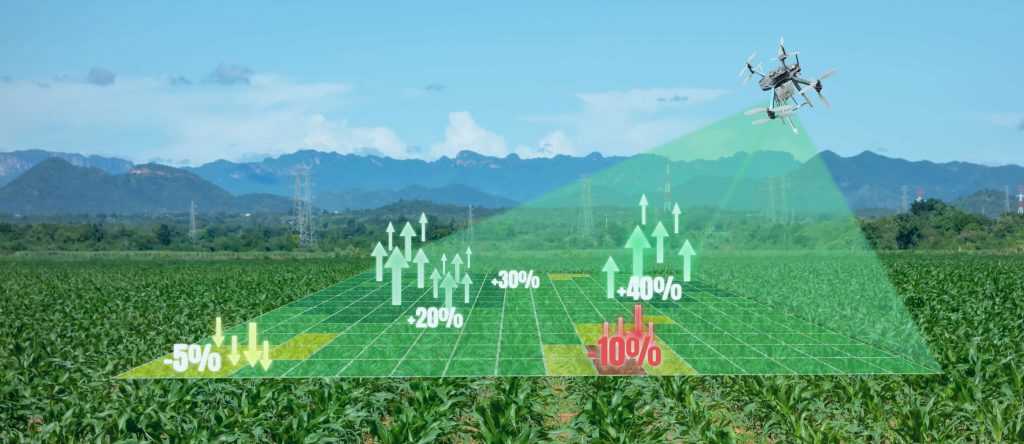
2.1. Crop Monitoring and Health Assessment
Drones equipped with multispectral or thermal sensors provide detailed images of fields.
These images help farmers detect issues like pest infestations, water stress, and nutrient deficiencies early.
2.2. Precision Farming
Drones enable targeted application of fertilizers, pesticides, and water.
This reduces costs and minimizes environmental impact by preventing overuse of chemicals.
2.3. Soil Analysis
Pre-planting, drones can generate 3D maps to analyze soil health and structure.
This information helps farmers plan better irrigation and fertilization strategies.
2.4. Irrigation Management
Thermal cameras on drones identify areas with water stress, ensuring efficient irrigation.
2.5. Crop Spraying
Drones can spray pesticides and fertilizers uniformly across fields.
This method is faster, safer, and more effective than manual spraying.
2.6. Livestock Monitoring
Drones assist in monitoring livestock in large or remote areas, ensuring their health and safety.
3. Benefits of Using Drones in Agriculture
3.1. Enhanced Efficiency
Tasks like field mapping and crop spraying, which traditionally take days, can be completed in hours.
3.2. Cost Reduction
Targeted applications of resources save money on inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
3.3. Improved Yields
Early detection of issues and precise resource allocation lead to healthier crops and higher yields.
3.4. Environmental Benefits
Reducing chemical overuse minimizes soil and water contamination.
Optimized resource use supports sustainable farming practices.
3.5. Better Data Collection
High-resolution data from drones helps farmers make informed decisions, improving overall farm management.
4. Challenges in Adopting Drones in Agriculture
4.1. High Initial Investment
The cost of drones and related software can be prohibitive for small-scale farmers.
4.2. Lack of Awareness
Many rural farmers are unaware of drone technology or its potential benefits.
4.3. Regulatory Hurdles
Strict regulations around drone usage can delay their adoption.
Farmers must obtain licenses and follow safety guidelines for drone operations.
4.4. Technical Skills
Operating drones requires training and technical know-how, which may not be readily available in rural areas.
5. Global Impact of Drones on Farming
5.1. Success Stories Worldwide
USA: Farmers use drones for large-scale precision agriculture to optimize yields.
Japan: Drones have replaced helicopters for crop spraying, reducing costs and emissions.
Africa: Drones are helping smallholder farmers combat pests and improve yields.
5.2. India’s Adoption of Drones
The Indian government has recognized the potential of drones and is promoting their use through initiatives like the Digital Agriculture Mission.
6. The Future of Drones in Rural Agriculture
6.1. Integration with AI and IoT
AI-powered drones can predict weather patterns, monitor crop growth, and automate tasks.
Integration with IoT devices will enable seamless farm management.
6.2. Affordable Models for Small Farmers
Manufacturers are developing cost-effective drones tailored for small-scale farming.
6.3. Government and NGO Support
Policies and subsidies are being introduced to make drones more accessible to farmers.
7. Case Study: Drones in Rajasthan’s Agriculture
7.1. Addressing Water Scarcity
In Rajasthan, drones are used for mapping water resources and optimizing irrigation.
7.2. Enhancing Crop Resilience
Farmers in arid regions use drones to monitor drought-resistant crops and identify pests early.
7.3. Community Training Programs
NGOs like Prakriti Kalyan Foundation are conducting workshops to educate farmers on using drones for sustainable farming practices.
8. Steps to Promote Drone Adoption in Agriculture
8.1. Awareness Campaigns
Educate farmers about the benefits and applications of drones through community programs.
8.2. Financial Assistance
Provide subsidies or low-interest loans to make drones affordable for small farmers.
8.3. Skill Development
Establish training centers to equip farmers with the knowledge to operate and maintain drones.
8.4. Public-Private Partnerships
Collaborate with tech companies to introduce customized solutions for rural farming needs.
Conclusion
Drones are revolutionizing agriculture by offering innovative solutions to traditional challenges, making farming more efficient, sustainable, and profitable. While the initial barriers to adoption remain, the potential benefits far outweigh the challenges.
Organizations like Prakriti Kalyan Foundation are playing a pivotal role in promoting sustainable farming practices by introducing technologies like drones to rural communities. As awareness grows and technology becomes more accessible, drones will undoubtedly shape the future of agriculture, ensuring food security and environmental sustainability for generations to come.

.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

0 Comments